基本原理
在事件传递的过程中设置一个中间对象,负责管理监听者和发送者,以达到解耦合的目的。
首先我们定义一个方法来注册监听对象,该对象包含节点(即作用域)、事件名和事件函数,然后我们在事件触发的时候调用触发函数,来触发所有监听该事件的对象。触发函数包含事件名和参数。
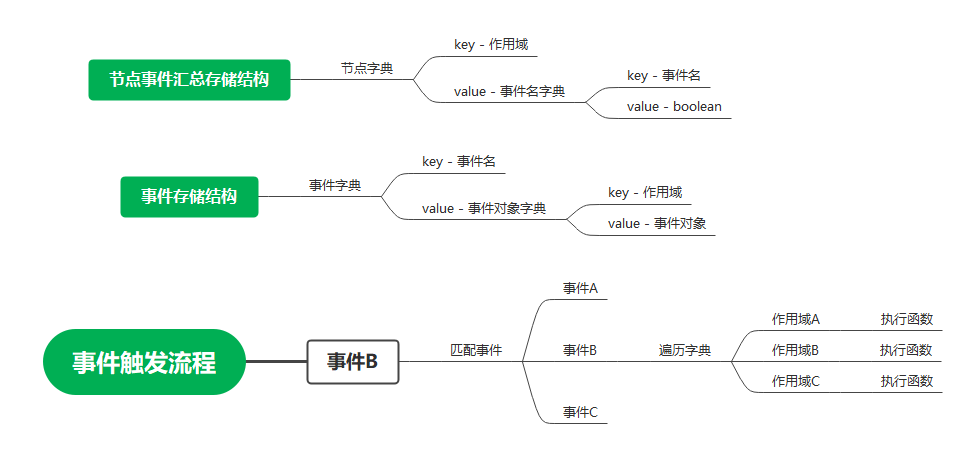
此处我们以字典 _eventDic 来存储监听对象,以事件名作为字典的 key,在字典里我们以作用域为 key 定义另一个字典,防止同名事件冲突以及同作用域事件重复添加。
同时,由于我们需要一个清除节点上所有事件的方法,因此我们单独设置一个字典 _nodeEventDic 用来保存节点和事件的关系。在清除节点上所有事件的时候只需要遍历该字典 _nodeEventDic 中对应作用域(传入的 node)的事件并且从事件字典 _eventDic 中查找对应的事件对象及其作用域即可。
具体的调用过程如下图所示:
这就是最基本的事件系统。
粘性通知
为了防止部分情况中出现通知不到位的情况(即先通知后监听),这里我们引入了粘性通知的功能。
此处我们定义一个字典 _stickyArr 来保存通知的内容,这里我们分为两种情况,一种情况是该粘性通知只需要通知一次,则我们只需要让新的通知覆盖旧的通知;另一种是需要多次通知,则我们设置一个数组来保存多次通知的内容。
粘性通知和普通通知的触发事件逻辑相似,可以说前半部分的代码和普通通知一样,只不过我们增设一个通知标识符,用于判断是否通知到位,若没有通知到位,则进入粘性通知内容保存的流程。
注册监听者的部分代码也有改动,在注册完成后,若从粘性通知字典 _stickyArr 取到对应事件名的内容,则立刻进行一次通知,通知结束后删除对应的内容。
简单来说,粘性通知就是在监听和通知这两个过程之后增加一个判断,对于监听者来说,就是要判断有无通知的内容,而对于通知来说,就是判断是否有监听者监听过该通知内容。
代码
事件数据类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| export default class EventInfo {
public node;
public event: Function;
public type: string;
constructor(node, type: string, event: Function) {
this.node = node;
this.event = event;
this.type = type;
}
}
|
事件管理类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
| import EventInfo from "../bean/EventInfo";
export default class EventManager {
private static _eventId = 1;
private static _eventDic = {};
private static _nodeEventDic = {};
private static _stickyArr = {};
public static dispatchEvent(type, data): void {
for (let key in this._eventDic[type]) {
let event = this._eventDic[type][key] as EventInfo;
event.event.call(event.node, data);
}
}
public static dispatchEventSticky(type, data, isArr?) {
let eventOk = false;
for (let key in this._eventDic[type]) {
let event = this._eventDic[type][key] as EventInfo;
event.event.call(event.node, data);
eventOk = true;
}
if (!eventOk) {
if (isArr) {
if (!this._stickyArr[type]) {
this._stickyArr[type] = [];
}
this._stickyArr[type].push(data);
} else {
this._stickyArr[type] = data;
}
}
}
public static onEvent(node, type: string, event: Function) {
var obj = new EventInfo(node, type, event);
if (!this._eventDic[type]) {
this._eventDic[type] = {};
}
if (node.eventId == undefined) {
node.eventId = "event_" + this._eventId++;
}
this._eventDic[type][node.eventId] = obj;
let data = this._stickyArr[type];
if (data) {
if (data.length) {
let event = this._eventDic[type][node.eventId] as EventInfo;
for (let i = 0, len = data.length; i < len; i++) {
event.event.call(event.node, data[i]);
}
delete this._stickyArr[type];
} else {
let event = this._eventDic[type][node.eventId] as EventInfo;
event.event.call(event.node, data);
delete this._stickyArr[type];
}
}
if (!this._nodeEventDic[node.eventId]) {
this._nodeEventDic[node.eventId] = {};
}
this._nodeEventDic[node.eventId][type] = true;
}
public static offAllEventByNode(node) {
if (!node || !this._nodeEventDic[node.eventId]) return;
for (let key in this._nodeEventDic[node.eventId]) {
delete this._eventDic[key][node.eventId];
if (Object.keys(this._eventDic[key]).length == 0) {
delete this._eventDic[key];
}
}
delete this._nodeEventDic[node.eventId];
}
}
|

其他版本
Unity 版本